Can you guess how many jelly beans are in the jar below?
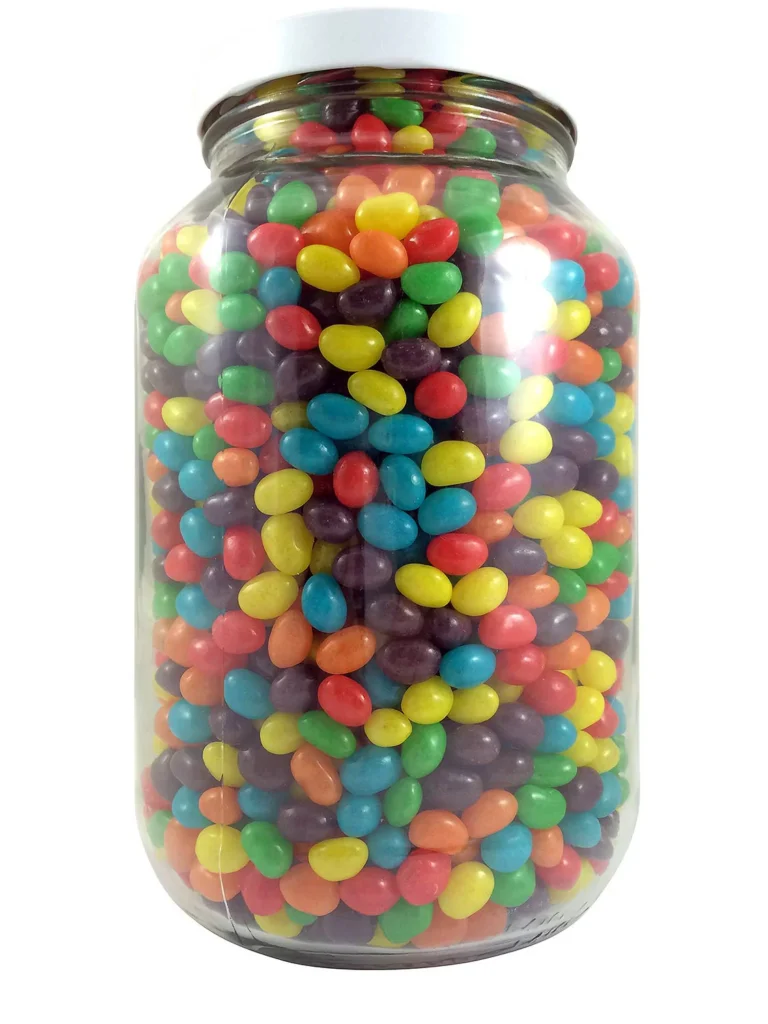
Challenges/puzzles like this, where you’re asked to estimate the number of jelly beans in a jar to win a prize, are quite common.
While there are scientific methods to get precise results, there’s rarely enough time to do all the math.
Instead, these challenges are designed to test your estimation skills and explore the strategies people use to arrive at their guesses.
If you find yourself in one of these challenges, what strategy can help you make an accurate estimate?
Here are six excellent methods you can use to get closer to the right number.
Method #1: Volume Calculation
The first approach to estimating the number of jelly beans in a jar is by calculating the volume.
You can do this in two ways, depending on the situation: precise volume calculation or a quicker, casual estimation.
If you have time and are aiming for accuracy, the precise method is recommended.
However, if you’re in a quick challenge, like those often found in casual contests, the second, more informal method is faster and more practical.
Let’s take a closer look at both methods.
I. Precise method
Estimating the number of jelly beans in a jar using volume calculation method involves calculating both the volume of the jar and the jelly beans. Here’s a detailed approach:
- Step 1: Measure the dimensions of the jar, focusing on its height and diameter. These measurements are essential for the next step.
- Step 2: Calculate the volume of the jar using the formula for the volume of a cylinder: V=πr2h,where r is the radius (half the diameter) and h is the height of the jar.
- Step 3: Estimate the volume of a single jelly bean, approximately 0.06544 cubic inches, as a baseline.
- Step 4: Since jelly beans don’t perfectly stack together, account for the void space between them. Typically, about 22% of the jar will be empty due to the irregular shape of the beans. Adjust for this by multiplying the jar’s volume by 0.78 to represent the filled space.
- Step 5: Divide the adjusted volume of the jar by the volume of a single jelly bean to estimate the total number of jelly beans in the jar.
II. Casual Method
Alternatively, you can estimate casually by counting the number of jelly beans across the bottom of the jar (as close to the center as possible).
Use this as your radius, r, then apply the formula πr2 to estimate how many beans cover the bottom.
Next, count the layers of beans up the sides of the jar. Multiply the base layer estimate by the number of layers for a quick jelly bean count.
Method #2: Layer Counting Method
Another quick way to estimate the number of jelly beans is by counting them in layers.
- Step 1: Count Jelly Beans across the Bottom: Start by counting how many jelly beans fit across the diameter of the jar. For example, if 10 jelly beans fit across the bottom, this gives you a radius of 5 jelly beans (half the diameter). This count represents the base layer of beans.
- Step 2: Estimate the Base Area To get a more accurate estimate of how many jelly beans are at the bottom of the jar, use the formula for the area of a circle, πr2 , where r is the radius in jellybeans. If 10 jelly beans fit across, the radius is 5 jelly beans. Using the formula πr2, you can calculate the area of the base in terms of jelly beans. For example, with a radius of 5 jelly beans: Area=π×52=π×25≈79 jelly beans This gives you an estimate of how many jelly beans cover the base of the jar.
- Step 3: Count the Number of Layers: Now, count how many layers of jelly beans are stacked from the bottom to the top of the jar. If the jar has 10 layers, this number will help you determine the total jelly bean count.
- Step 4: Calculate the Total Estimate: Multiply the number of jelly beans across the bottom by the number of layers. For example, if there are 79 beans across the bottom and the number of layers is10 layers, the total estimate would be: Total=79 beans across×10 layers=790 jelly beans
Method #3: Midline Counting Method
This method involves drawing imaginary lines through the center of the jar to estimate the number of jelly beans by calculating the jelly beans along three dimensions: width, depth, and height:
- Step 1: Count Jelly Beans Across the Middle (Width): Begin by visually drawing an imaginary horizontal line across the middle of the jar. Count how many jelly beans intersect this line from side to side. This number represents the width of the jar in terms of jelly beans.
- Step 2: Count Jelly Beans Across the Adjacent Side (Depth): Next, imagine another horizontal line running across the adjacent side of the jar. Count the jelly beans that intersect this line, which gives you the depth measurement in jelly beans.
- Step 3: Count the Vertical Jelly Beans (Height): Now, draw an imaginary vertical line from the bottom to the top of the jar, again passing through the center. Count how many jelly beans are stacked along this line, giving you the height of the jar in jelly beans.
- Step 4: Multiply the Three Counts: Finally, multiply the three numbers together (width, depth, and height) to estimate the total number of jelly beans. For example, if there are 8 jelly beans across the middle, 6 along the adjacent side, and 10 jelly beans going vertically, you can calculate the total as: Total=8×6×10=480 jelly beans
@markrober Losers pick up.
♬ original sound – Mark Rober
Method #4: Average of Visible Beans
The Average of Visible Beans method is a straightforward way to estimate the number of jelly beans in a clear jar. Here’s a detailed breakdown with examples:
- Step 1: Count Visible Jelly Beans: Begin by counting the number of jelly beans visible in a specific area of the jar. For instance, if you can see 12 jelly beans in a small section of the jar, take note of this count.
- Step 2: Estimate Similar Areas: Next, estimate how many similar areas exist in the jar. If the jar is cylindrical and you can see 20 similar sections around the jar, you can use this to project your count.
- Step 3: Calculate Total Estimate: Multiply the count from the visible area by the number of similar areas to get a rough estimate. Using our example: Total=12 visible beans ×20 similar areas =240 jelly beans
Method #5: The Fist Estimation Strategy
This unconventional method entails using your fist to estimate the number of jelly beans in a jar. While it may sound imprecise, it has proven effective in many casual jelly beans estimation contests.
- Step 1: Estimate Jelly Beans per Fist: Start by getting close to the jar and placing your fist against it. Mentally estimate how many jelly beans would fit in the size of your fist. For instance, you might guess that around 20 jelly beans fit into the volume of your fist.
- Step 2: Estimate How Many Fists Fit in the Jar: Next, estimate how many times your fist would fit inside the jar, both across the bottom and up the sides. This gives you a rough sense of how many “fistfuls” of jelly beans could fit in the jar. If you think your fist fits 8 times across the jar’s base and 10 times up the height, you now have an estimate of the number of “fists” inside the jar.
- Step 3: Multiply for Final Estimate: Multiply the number of jelly beans you estimated per fist by the total number of fists that would fit in the jar. For example, if your fist holds 50 jelly beans and fits approximately 10 times in the jar, your estimate would be: Total=50×100=500 jelly beans
Method #6: Wisdom of the Crowd
If the guessing is part of a contest or group activity:
- Step 1: Gather guesses from a group of people.
- Step 2: Use the average or median of these guesses to arrive at a more balanced estimate, as collective wisdom can often yield a more accurate number than individual guesses.
As you can see, estimating the number of jelly beans in a jar can be both fun and challenging. Whether you choose the Volume Calculation, Layer Counting, Fist Estimation Strategy, Average of Visible Beans, or Wisdom of the Crowd, each technique offers unique advantages. Experiment with these methods for an engaging guessing game!
